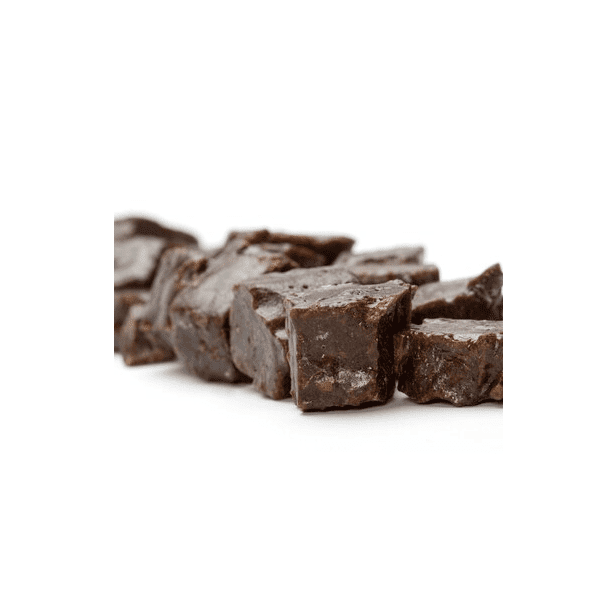
Asafoetida
Global Market Demand
Asafoetida exporter in India exports asafoetida to around 114 countries and territories in the world. The combined value of total Asafoetida import from India is 7.93 USD million. The growing popularity of Asafoetida worldwide is due to its several healthy and medicinal uses. Asafoetida is used for curing and preventing health conditions such as breathing or throat problems, digestion problems, to restart their menstrual periods after menstruation by women, and so on.
Specification
| Product Name | Asafoetida |
|---|---|
| Origin | PeruCentral Asia, eastern Iran to Afghanistan |
| Family | Umbellifers |
| Binomial name | Ferula assafoetida |
Ingredients
| Nutrients | Calories 297.1 Carbohydrates 67.8g Fiber 4.1g |
|---|---|
| Minerals | Calcium Iron Magnesium Phosphorous Zinc Copper Manganese |
| Protein | 4 g |
| Fats | Fat 1.1g |
Uses & Benefits
Uses :
foods.com/img/icon-img/point.png) Asafoetida has many health benefits. It is used to reduce bloating and such other digestion and stomach problems.
Asafoetida has many health benefits. It is used to reduce bloating and such other digestion and stomach problems.foods.com/img/icon-img/point.png) Asafoetida is also known to be a natural source to lower blood pressure levels. It is a blood thinner and is packed with a compound called coumarin that aids in improving blood flow.
Asafoetida is also known to be a natural source to lower blood pressure levels. It is a blood thinner and is packed with a compound called coumarin that aids in improving blood flow.foods.com/img/icon-img/point.png) Asafoetida is also said to heal insect and animal bites. It is also known to reduce menstrual pain and headaches.
Asafoetida is also said to heal insect and animal bites. It is also known to reduce menstrual pain and headaches.foods.com/img/icon-img/point.png) Asafoetida is also sometimes applied directly to the skin for corns and calluses. But no scientific evidence has supported this use.
Asafoetida is also sometimes applied directly to the skin for corns and calluses. But no scientific evidence has supported this use.

 Mail
Mail 

